***** Second Hour *****
Memory:
Memory is internal storage areas in the computer. The term memory identifies data storage that comes in the form of chips, and the word storage is used for memory that exists on tapes or disks. Moreover, the term memory is usually used as shorthand for physical memory, which refers to the actual chips capable of holding data. Some computers also use virtual memory, which expands physical memory onto a hard disk.
Every computer comes with a certain amount of physical memory, usually referred to as main memory or RAM. You can think of main memory as an array of boxes, each of which can hold a single byte of information. A computer that has 1 megabyte of memory, therefore, can hold about 1 million bytes (or characters) of information.
Classification of Memory:
There are two types of memory is used in computer –
- Main Memory / Primary Memory / Internal Memory
- Auxiliary Memory / Secondary Memory / External Memory
Main Memory:
Which memory is directly related with CPU is called Main memory. Presently, ROM and RAM are used as main memory in micro computer.
Types of Main Memory –
- Magnetic Core Memory
- Thin Film Memory
- Semiconductor Memory (RAM – DRAM and SRAM, ROM, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM)
- Magnetic Bubble Memory
- Charge Coupled Memory
ROM (read-only memory): Computers almost always contain a small amount of read-only memory that holds instructions for starting up the computer.
RAM (random-access memory) / Firmware: This is the same as main memory. When used by itself, the term RAM refers to read and write memory; that is, you can both write data into RAM and read data from RAM. This is in contrast to ROM, which permits you only to read data. Most RAM is volatile, which means that it requires a steady flow of electricity to maintain its contents. As soon as the power is turned off, whatever data was in RAM is lost.
PROM (programmable read-only memory): A PROM is a memory chip on which you can store a program. But once the PROM has been used, you cannot wipe it clean and use it to store something else. Like ROMs, PROMs are non-volatile.
EPROM (erasable programmable read-only memory): An EPROM is a special type of PROM that can be erased by exposing it to ultraviolet light.
EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory): An EEPROM is a special type of PROM that can be erased by exposing it to an electrical charge.
External Memory:
External memory or Secondary memory is permanent storage, which is nonvolatile. The capacity of storage device is measured in bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes and terabytes etc.
Because RAM exists through electricity, when you turn off the power to your computer, data in RAM disappears. Therefore, before you turn off the microcomputer off, you must save your work onto a storage device that stories data magnetically (permanently) – such as a diskette or a hard disk – rather than electrically. When store on a secondary storage device, your data will remain intact even when the computer is turned off.
In addition to data, computer software must be stored in a computer usable form. A copy of software instructions must be retrieved from a permanent storage device and place into RAM before processing can begin.
Types of Secondary Memory –
- Magnetic Disk (HDD, FDD)
- Optical Disk
- Magnetic Tape Drive
Disk: Disk is a storage data device. A disk is used to store data.
Memory Unit |
||
| 0, 1 | = | BIT or Binary Digit |
| 8 BIT | = | 1 Byte |
| 1024 Byte | = | 1 Kilobyte (KB) |
| 1024 KB | = | 1 Megabyte (MB) |
| 1024 MB | = | 1 Gigabyte (GB) |
| 1024 GB | = | 1 Terabyte (TB) |
| 1024 TB | = | 1 Petabyte (PB) |
| 1024 PB | = | 1 Exabyte (EB) |
Capacity of various storage devices: |
|||||
| HDD | FDD | Pen Drive | CD Disk | DVD Disk | RAM |
| 120 GB | 1.44 MB | 1 GB | 700 MB | 4.7 GB | 128 MB |
| 200 GB | 2 GB | 256 MB | |||
| 250 GB | 4 GB | 512 MB | |||
| 320 GB | 8 GB | 1 GB | |||
| 500 GB | 16 GB | 2 GB | |||
| 1 TB | 3 GB | ||||
| 2 TB | |||||
Hardware, Software and Firmware
Hardware: Hardware refers to the physical equipment of a computer system, such as – Input Device (Keyboard, Mouse etc.), System Device (Processor, Motherboard, RAM, Power Unit etc.), Output Device (Monitor, Printer etc.)
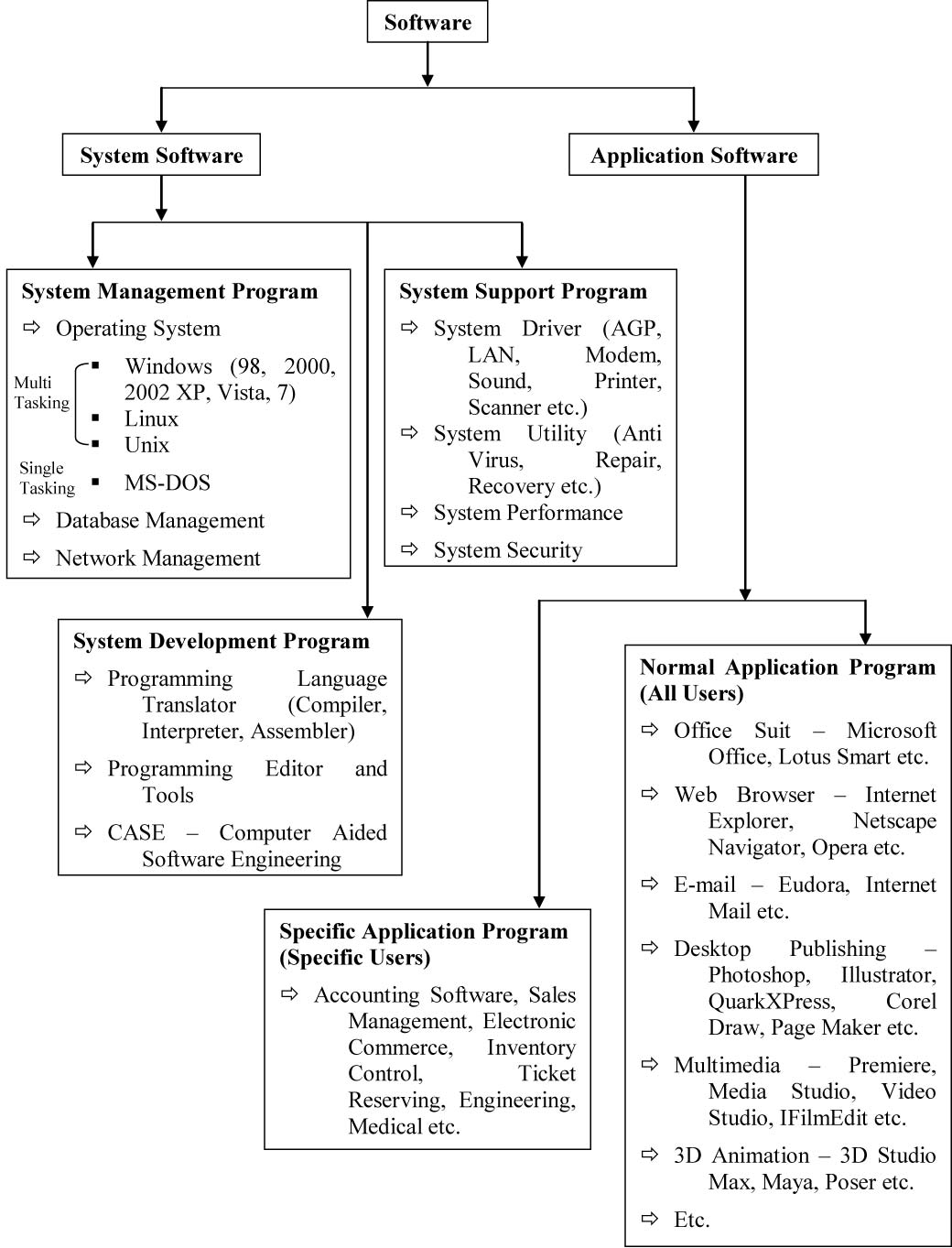
Software: Software refers to computer programs (a set of instructions) that contribute to the operations of a computer (hardware). As hardware is not self-sufficient, software has to provide the techniques and procedures to complete any task. Different types of software are available to solve various problems.
Firmware: Programs that are built in the factory; these are special instructions for computer operations, such as those that start the computer or put characters on the screen and it is cannot be written on or erased by the computer user.
Difference between Hardware and Software:
** The physical components of a computer are called hardware. Physical components may be electronic, electrical, magnetic, mechanical or optical. Examples of hardware are microprocessors and other ICs, hard disks, floppy disks optical disks, cathode ray tube(CRT), keyboard, printer, plotter, etc.
** A sequence of instructions given to a computer to perform a particular task is called a program. A set of programs written for a computer is called software. The software required to execute user’s program is known as system software. The term software includes both system software and user’s programs. The system software includes operating system, assembler, compiler, interpreter, debugging programs, text editors, etc. The operating system is a collecting of programs which controls the overall operation of a computer.